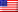
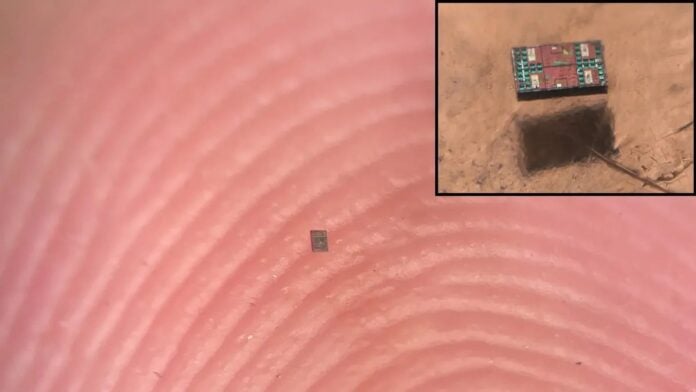
Researchers have created fully autonomous microrobots smaller than a grain of salt, capable of independent movement, sensing, and computation without external control. This represents a significant leap in nanotechnology, opening doors to applications in medicine, materials science, and beyond.
The Scale of Innovation
These robots, developed jointly by the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan, measure just 200-300 micrometers in length – thousands of times smaller than a millimeter. Despite their size, they integrate sensing capabilities, onboard processing, and movement mechanisms into a single, self-contained system.
Key to their operation is light-based power. Unlike traditional robots relying on motors, these devices manipulate fluid dynamics by generating electrical fields that propel ions, making them uniquely suited for microscopic environments. This eliminates the need for bulky mechanical components.
Independent Operation and Sensing
Previous microrobotic designs often required external guidance via magnetic fields or physical tethers. These new robots, however, incorporate miniature solar cells that power integrated processors, allowing them to respond to environmental cues and execute programmed tasks without human intervention.
The robots can detect temperature changes, navigate pre-defined paths, and communicate through patterned movements visible under a microscope. This level of autonomy has not been achieved before at such a small scale.
Potential Applications and Future Implications
The technology’s potential applications are broad:
- Biological Monitoring: Tracking cellular processes in real-time.
- Medical Diagnostics: Delivering targeted therapies or sensing diseases at the microscopic level.
- Micro-Assembly: Building complex nanoscale devices with precision.
- Environmental Sensing: Detecting pollutants or toxins in fluids.
Because the robots are inexpensive to mass-produce, the technology promises new avenues for research and development at previously unreachable scales.
The development of truly autonomous microrobots represents a fundamental shift in nanotechnology. By removing external dependencies, these devices unlock a new era of precision engineering and microscopic exploration.